Appearance
A Workflow Example
In this chapter, the set up of a workflow is described along a concrete example.
The example consist of 2 service calls whereas the second service processes the result of teh first service call.
The Combined Services
For this example 2 services will be combined in a workflow:
- stock time series service
- covariance generator
Both services have to be available, published and subscribed by an application.
Stock Time Series Service
This service downloads the values of a given stock for a given time window.
It takes as input data:
| Input Value | Description |
|---|---|
| stock_symbols | Array of stock names, e.g. ["IBM","AAPL"] |
| start_date | The day of the first stock value to be retrieved. Must be in form yyyy-mm-dd, e.g., 2022-01-01 |
| end_date | The day of the last stock value to be retrieved. Must be in form yyyy-mm-dd, e.g., 2022-02-02 |
It takes as input params:
- no params
It returns as output:
- A Json structure containing for each stock an array of date-value pairs.
Covariance Generator
This service computes the covariance within an array of values.
It takes as input data:
| Input Value | Description |
|---|---|
| time_series_data | A map of objects which contains a map of time/value pairs. |
It takes as input params:
| Input Value | Description |
|---|---|
| covariance_estimator | name of algorithm to be taken for computation of covariance |
| number_of_decimals | number of ... |
It returns as output:
- A Json structure containing the shrunk covariance matrix.
The Workflow
Create a new workflow service. Go to the details page and open the workflow model editor.
Create the following flow:
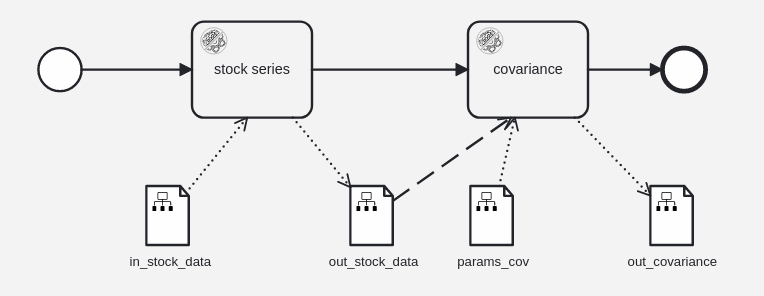
by doing the following steps:
- drag 2 service nodes into the editor
- assign the 2 services to the nodes
- click on the change type icon, open the list of PLANQK Service Tasks and select the proper service
- connect the nodes (start node -> service node -> service node -> end node)
- drag 4 data object nodes into the editor
- connect the 4 data object nodes to the service nodes as shown in picture
There is nothing to configure for the service nodes, but we need to configure the input/output data of the data object nodes.
Configure the first data object node (in_stock_data):
- Click on the first data object node. On the right side of the editor you find the context menu for this node.
- Enter "in_stock_data" as name of the node.
- Each data node must have a name. The name should not have white spaces within.
- Click on the plus-button of the content param. Enter
start_dateas name and${wf_sd}as value. With this configuration you can later pass the start date as parameterwf_sdto the workflow. - Click again on the plus-button of the content param. Enter
end_dateas name and${wf_ed}as value. With this configuration you can later pass the end date as parameterwf_edto the workflow. - Click again on the plus-button of the content param. Enter
stock_symbolsas name and${wf_stsy}as value. With this configuration you can later pass the array of stock symbols as parameterwf_stsyto the workflow.
Configure the second data object node (out_stock_data):
- Click on the second data object node to open the context menu for this node.
- Enter "out_stock_data" as name of the node.
- Leave the content mapping blank.
- Click on the connection line to the covariance service and change the type of the connection to "transformation association".
- In the context menu of this line, click on the plus-button of the Expressions param. Enter
time_series_dataas name and${out_stock_data.jsonPath("$").element()}as value. With this configuration the result of the stock series service, which is a json-object, will be parsed and the content will transformed into the time_series_data parameter which is needed by the covariance service.
Configure the 3rd data object node (params_cov):
- Click on the 3rd data object node to open the context menu for this node.
- Enter "params_cov" as name of the node.
- Click on the plus-button of the content param. Enter
paramsas name and{"covariance_estimator": "LedoitWolf","number_of_decimals": 4}as value. We now have hard coded the configuration for the service how to compute the covariance result.
Configure the 4th data object node (out_covariance):
- Click on the 4th data object node to open the context menu for this node.
- Enter "out_covariance" as name of the node.
- Leave the content mapping blank.
Save, Publish, and Subscribe
At the end, click on the save button to store the edited workflow in your workflow service.
NOTE
There is no automatic save or intermediate save, so be aware to not lose you edit work by just leaving the editor without saving your work.
When the workflow is ready, it has to be deployed to the deployed to the workflow engine. Click on the Deploy button.
Now you can leave the editor and go back to the details page of your service. To trigger an execution of the workflow, the service has to be published (internal or to marketplace). After it is published you can create an application and subscribe to this service.
Start the Service
Now you can trigger an execution of the workflow via the OpenAPI-UI of your application.
As the POST call expects some input params, you have to pass a structure, containing the 3 configured parameter wf_stsy, wf_sd and wf_ed. This is an example of how the request body may look like:
json
{
"data": {
"wf_stsy": {
"value": "[\"IBM\",\"AAPL\"]",
"type": "String"
},
"wf_sd": {
"value": "2022-01-02",
"type": "String"
},
"wf_ed": {
"value": "2022-01-15",
"type": "String"
}
}
}If the workflow was executed without errors you can request the result via the GET/{id}/result endpoint which you find further below in the OpenAPI-UI.
The result contains an array of variables. Within this array, not only the output variables are listed, but also all input parameters and all intermediate data which are created during the workflow execution.
For this example, the result should contain:
| variable name | description | example content |
|---|---|---|
| wf_stsy | the stock symbols for the first service passed as input param to the workflow execution | ["IBM","AAPL"] |
| wf_st | the start date for the first service passed as input param to the workflow execution | 2022-01-01 |
| wf_ed | the end date for the first service passed as input param to the workflow execution | 2022-01-05 |
| out_stock_data | the result of the first service | "AAPL": { "2022-01-01": 179, "2022-01-01": 180 } ... |
| time_series_data | the transformed out_stock_data which is then passed as input param to the second service | "AAPL": { "2022-01-01": 179, "2022-01-01": 180 } ... |
| out_covariance | the result of the second service | "shrunk_cov_matrix": { "AAPL": { "AAPL":0.001 }, ... } |